In the world of software development, managing configurations is a critical aspect of building robust and scalable applications. One popular method for handling configurations is through the use of .env files.
These files allow developers to store sensitive information, such as API keys, database credentials, and environment-specific settings, separate from the codebase. In this article, we will explore the ins and outs of .env files, from creating them to configuring their contents effectively.
What is a .env File?
A .env file, short for “environment,” is a simple text file that contains key-value pairs of configuration variables. These variables are typically used to store settings that can vary depending on the environment in which the application is running, such as development, testing, or production. The advantage of using .env files is that they provide a way to keep sensitive information secure and separate from the source code, thus enhancing security and maintainability.
Creating a .env File
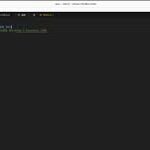
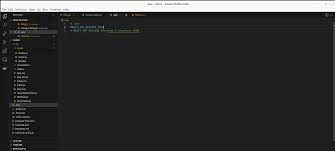
To create a .env file, you can simply use a text editor like Notepad, Visual Studio Code, or any other plain text editor. Each configuration variable is defined on a new line in the format KEY=VALUE. For example:
API_KEY=your_api_key_here
DB_HOST=localhost
DB_USER=admin
DB_PASSWORD=secret_passwordOnce you have defined the necessary configuration variables in your .env file, you can save it in the root directory of your project.
Configuring .env Files in Different Environments
One of the key benefits of using .env files is the ability to configure different values for the same variables in different environments. For instance, you may have separate .env files for development, testing, and production environments, each containing environment-specific values for the configuration variables. This allows you to maintain consistency across environments while tailoring settings to each specific context.
Loading and Accessing .env Variables in Your Application
To make use of the configuration variables stored in your .env file, you need to load them into your application. This can be done using various libraries and tools depending on the programming language and framework you are using. For instance, in a Node.js application, you can use the dotenv library to load the .env file and access the variables like so:
require('dotenv').config();
const apiKey = process.env.API_KEY;
const dbHost = process.env.DB_HOST;By loading the .env file in your application, you can securely access the configuration variables without hardcoding sensitive information into your code.
Best Practices for Working with .env Files
When working with .env files, it is essential to follow some best practices to ensure the security and maintainability of your application:
- Keep
.envFiles Out of Version Control: To prevent exposing sensitive information, ensure that.envfiles are listed in your project’s.gitignorefile so that they are not accidentally committed to the repository. - Use Descriptive Variable Names: Choose meaningful names for your configuration variables to improve readability and maintainability.
- Update
.envFiles Regularly: As your application evolves, make sure to update and review your.envfiles to reflect changes in configurations and settings. - Store
.envFiles Securely: Treat.envfiles as sensitive information and store them securely, using encryption or access controls as necessary.
Conclusion
Mastering .env files is a valuable skill for any developer looking to build secure and flexible applications. By creating and configuring .env files effectively, you can manage configurations seamlessly across different environments while keeping sensitive information safe and separate from your codebase. Remember to follow best practices, such as keeping .env files out of version control and using clear variable names, to ensure the reliability and security of your applications. So, go ahead, harness the power of .env files, and take your configuration management to the next level!